A lean startup is about getting to market fast, experimenting, iterating and learning, all with minimal resources. By using continuous testing and customer feedback, lean startups can adapt and pivot as needed, reducing waste and increasing chances of success. Lean methodology enables the type of supercharged, nimble venture that many beginning entrepreneurs yearn for.

Image via OpenVerse
Introduction
John Krafcik first used the phrase “Lean production” in 1988, to praise the virtues of efficient, low waste car manufacturing systems. Eric Ries’s 2011 book “The Lean Startup” evolved the idea. He went beyond “lean” principles of manufacturing cost cutting, to emphasize an adaptable product development process that systematically experiments and learns. Its nimbleness comes from its core principles: testing hypotheses, responding to customer feedback, rapid prototyping, validated learning, and iterative design. Eric Ries coined terms such as the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop and the minimum viable product (MVP) and pivot.
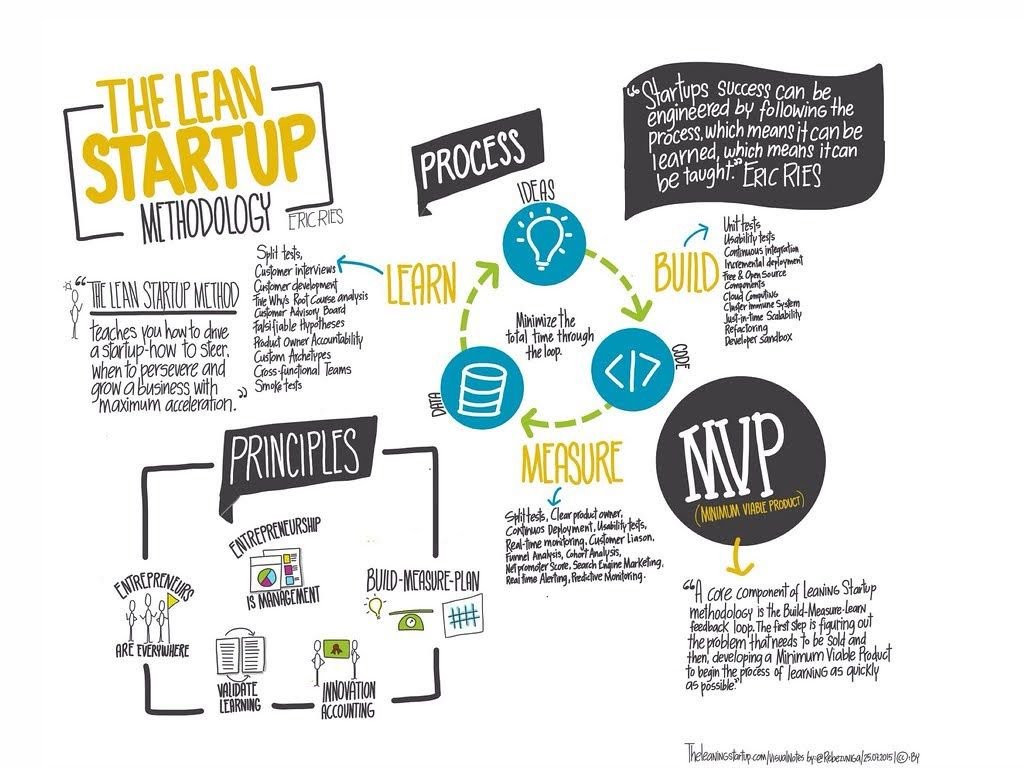
Image via OpenVerse
The Impact of Lean Methodology
Lean Methodology’s top benefits are efficiency, adaptability, and speed. Moreover, its data driven learning approach and customer focus ensure that lean startups always aim towards product-market fit. Adoption of lean methodology varies by industry and company culture. Industries that emphasize efficiency (for example manufacturing, healthcare, and software) are among its greatest adopters and champions. However, adaptability stands out as the most powerful benefit of lean product development. Adaptability allows companies to reach success faster by “feeling their way” in the market through experimentation and learning. After their initial success, lean startups remain competitive by continuously adjusting. Last but not least, pivots are the larger, strategic moves needed in the face of significant challenges. For all these reasons, Lean thinking can be credited for the success of some of the most resounding names in entrepreneurship.
Examples
Dropbox, Airbnb, Mailchimp, Instagram, Netflix, and Youtube all illustrate the strengths of lean startups. They share some of the same ingredients: they started small, then continuously improved based on user and market data. Some had remarkable pivots, all expanded in a customer-focused way.
For example, Dropbox started as a demo video, Airbnb as a personal house-rental, Mailchimp was a side project. Instagram pivoted from a location-based check-in app to a photo-sharing platform, based on user interest. Netflix evolved from DVD rental by mail to a streaming service that disrupted home entertainment. Youtube switched from a dating site to video-streaming.
Steps toward success
- Get Started: Find a customer problem to solve. Build a minimal viable product (MVP) that does just enough for you to test hypotheses, adjust and get a foot in the market.
- Learn: Do it fast and in a customer-centric way: Collect feedback and act on it. Iterate continuously and, if needed, know to pivot.
- Take off – Build a Team: People matter so make sure to assemble a team who has the right mindset., dedicated team.
- Fund Your Startup: also benefits from an agile, lean approach. Lean startups often opt for bootstrapping, crowdfunding, and other creative funding options.
Additional Reading
Here are some seminal books and articles documenting the lean startup journey:
- “The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses” by Eric Ries – contains a comprehensive guide to the lean startup approach. It lays out its core principles and leverages the author’s own experiences to illustrate its main points.
- “Lean Startup: A Comprehensive Historical Review” by Rafael Fazzi Bortolini and Marcelo Nogueira Cortimiglia – This article weaves a historical narrative connecting the lean startup concepts with previous theories and business practices.
- “Why the Lean Start-Up Changes Everything” by Steve Blank – contrasts traditional business planning and development with lean startup methodology, emphasizing its revolutionary contributions.
