
Source: Pixabay
Funding—why is it important?
Most companies, whether start-ups or established, require funding at some point, depending on their type and size. The funding is the money that investors put into a company to start and run its operations until a positive cash flow is established.
Especially for start-ups, funding is crucial for developing their products and services, hiring employees, marketing, establishing office buildings, and running day-to-day operations. Recent start-up statistics show that inadequate funding is why most start-ups close.
Further, inputting capital is essential for high-growth companies to maintain growth until it becomes profitable. The fundraising process can be monotonous and often time-consuming, but all founders must go through it to take off their business on time.
Types of Funding
There are various types of funding available for small businesses and companies. The five major types of funding, their sources, and essential aspects are presented below in a nutshell.
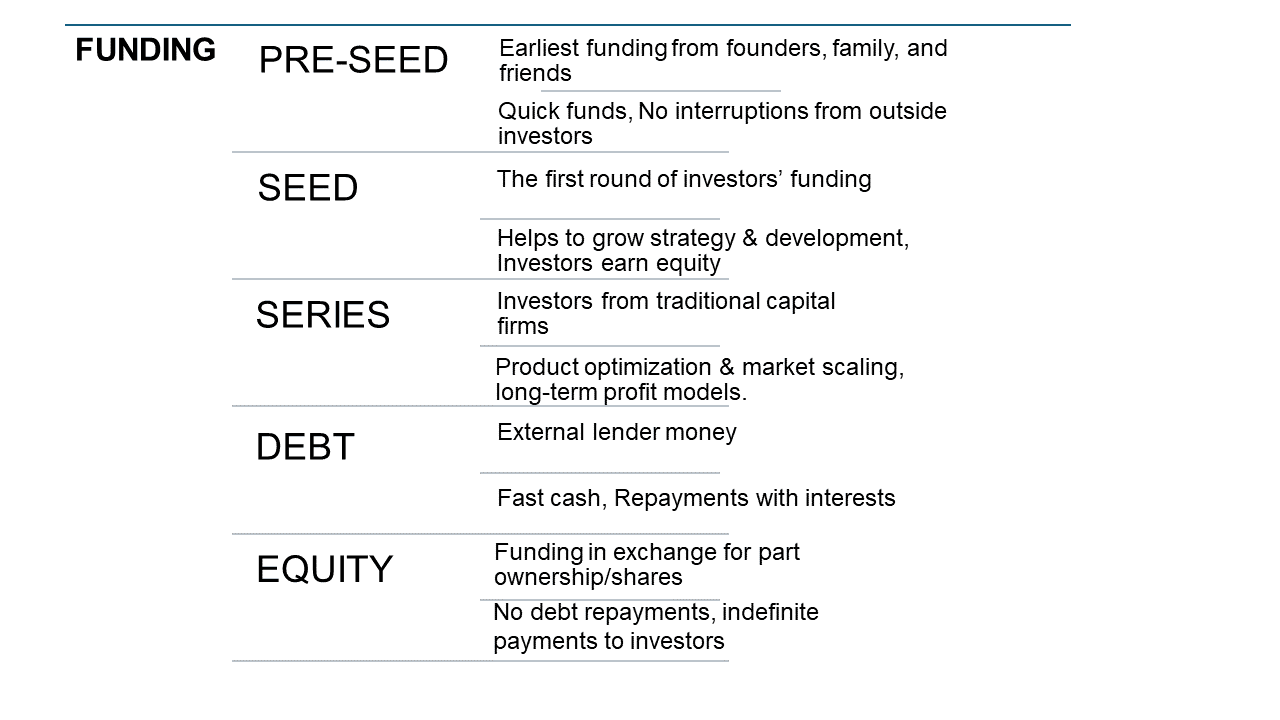
Source: Created by Author
1. Pre-seed Funding:
Pre-seed funding is the earliest stage of start-up funding and can be considered as an investment in a business’s idea. This kind of funding is an ideal choice when there is a winsome idea and a working prototype.
Companies can get pre-seed funding when they have a solid founding team and a minimum viable product that appeals to a target market and already has customers or has started attracting customers. The essential steps to follow through to secure pre-seed funding include putting together a strong pitch deck with all product details, the target market, the budget for the business, etc., to convince investors to invest in a company with little or no momentum. In most cases, pre-seed funding comes from the founder’s personal income, family, or friends, and in that case, will have more freedom in decision making and direction of the work without any external interventions.
2. Seed Funding:
After the validation of the start-up idea and prototype completion, it’s now time to get the business up and running. This is where the company looks for the seed money, generally a modest sum raised in the initial stages of a start-up or company to meet its initial expenses, such as its business plan and basic operating expenses.
Unlike the pre-seed funding stage, the company should have established revenue traction in order to get seed funding. At this stage, the company’s primary goal is to establish a minimum viable product and successfully maneuver through this initial stage to attract more financing from investors such as banks, start-up accelerators, incubators (for early-stage start-ups), and angel investors (with high personal wealth). Seed funding investors earn equity for their shares. America’s Seed Fund, backed by the National Science Foundation, invests up to $2 million with no equity in technology start-ups.
3. Series Funding:
After seed funding comes the series funding rounds to generate additional funding for product optimization and scale-up. Companies should have long-term profit models and clear-cut strategies for their products/services to secure financial support by this time. Depending on the business level, many series funding may become necessary, such as series A, B, C, etc. During series A, a start-up may sell off more of its stock for extra cash. At this stage, companies may not be generating net profit except that they will have some kind of revenue. Series A funding, often from traditional investors, angels, accelerators, or venture capitalists, can bring in a good amount of money. Series A is followed by series B funding, if funding is still needed to thrive in the market. The company might be successful by this time, so the funding will be used for scaling up rather than development. Series C funding is awarded only to successful companies and is meant to widen the horizons of the company in the market. Private equity firms, investment banks, etc., show interest in funding at this stage, which is considered the final stage of funding for most start-ups.
4. Debt Financing:
As the name implies, debt financing involves borrowing money from investors under the condition of repayment of this money along with interest within a specified time. The loans may be short- or long-term in the repayment schedule, depending on the type of application. The debts/loans can be borrowed from a variety of sources, including:
i) Friends or relatives, in the form of debt capital at the low interest rate. A formal loan document needs to be executed.
ii) Finance companies are a place to look for when companies fail to secure funding from other commercial sources. However, collateral (a valuable asset that can be attached to the loan in case of a loan default) may be necessary to secure funding.
iii) Banks/commercial lenders:
Apart from being a popular financing option, a solid business plan, a good track record, and a need for huge collateral make it a far-isolated option for start-ups. However, once the business is established with some net worth, cash flow, and profit and loss statements, bank/commercial lender funding can be the way.
iv) Government funding:
All three government bodies—federal, state, and local—have funding programs to support small businesses and newly founded ventures. Examples include the Small Business Administration and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Rural Development.
5. Equity Financing:
This type of financing involves exchanging a portion of the business ownership with the company’s financial investors, and the profit is thus shared with the investor. This is a permanent investment in the company, not to be repaid.
Examples of equity include membership units in the case of a limited liability company (LLC) or stocks such as in a corporation. Crowdfunding, angel investors, and venture capitalists fall under equity funding. Crowdfunding is a way to ask a large crowd to invest in the company’s idea or product. It is a good way to measure an idea’s reach in the market as a potential way to get funding in a short time span. Kickstarter and Indiegogo are two popular crowdfunding platforms. Private investors/angel investors can contribute funds to a business for a share in the business profit and equity. Large corporations that can invest huge amounts in start-up businesses are known as venture capitalists. In return, they often require a large share of the business. Companies receiving investor funds at some point are destined to go public or sell to pay back their investor’s money.
Apart from the above categorized funding options, entrepreneurs can look for grants to start or accelerate their businesses. A few popular options are listed below:
- Grants.gov—Federal grants from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Small Business Innovation Research Program—Federal grants to support science and technology innovations.
- Economic Development Administration Grants—Grants aimed to support regional economies through innovation.
- FedEx small business grants—Grants from FedEx to innovative small business models.
- Cartier Women’s Initiative award—Promotes eco-friendly and sustainable woman-owned businesses globally.
Conclusion
Securing funding at the right time is very important for any business and requires much time and effort. Many kinds of funding are available for companies at any stage, and information about major funding types and resources, including grants for a business owner or start-up founder, is discussed.
