How can work be optimally designed to maximize employee engagement and performance? An organization’s systematic and deliberate work allocation to individuals and groups is known as “job design,” a psychological theory of motivation. A job design theory that aims to pinpoint the essential elements that provide employees with a fulfilling, engaging, and stimulating work environment is the Job Characteristics Model (JCM).
Being developed by Richard Hackman and Greg Oldham in 1976 and 1980, the model has found widespread application as a framework for job analysis and job design research.
Encouraging and retaining employees is challenging for managers and HR professionals, as happy and engaged workers are more content and productive. The organization’s roles will become more attractive, demanding, and inspiring with the help of the job characteristics model.
The Design of Job Characteristics Model
According to the model, five key job characteristics (skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback) influence three critical psychological states (experienced meaningfulness, experienced responsibility for outcomes, and knowledge of actual outcomes), thereby influencing work outcomes (performance, satisfaction, motivation, etc).
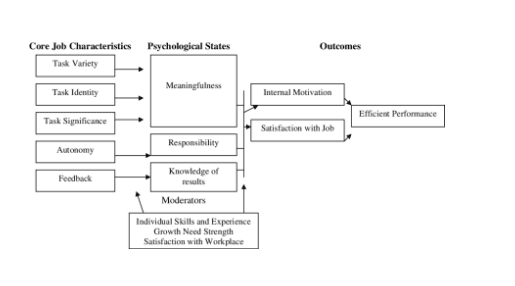
FIGURE 1 – uploaded by Karen Seashore Louis
The core job characteristics model has determined five characteristics responsible for generating the essential psychological states for employee motivation.
Skill Variety
The skill variety of a job refers to how many skills and abilities are required. This indicates that workers are involved in various tasks requiring multiple business operations competencies. For instance, a project manager might need to use project management software, effectively interact with team members, and conduct data analysis to make wise decisions.
To understand it, let’s compare two people with distinct occupations. Job A involves a lot of repeated activities and routines, but the work itself is simple. It only calls for a bit of talent or skill. However, Job B is more complex and calls for various skills. Who among the following workers will most likely find their employment meaningful? Since Job B requires multiple skills, this one will likely find meaning and novel situational experiences while working on the job.
Task Identity
Task identity refers to the degree to which a job involves completing a whole, identifiable work. Employees will be able to see their labor efforts and understand how their work fits into the organization’s larger objectives according to business management. For example, the procurement of raw materials, production, and customer delivery can all be managed by a supply chain manager. Job satisfaction and motivation are raised when an individual has a task identity because it cultivates a sense of pride and ownership in their work.
Task Significance
A task’s significance is the contribution it makes to the lives or work of others. A Job Characteristics Model highlights that workers in business should recognize the value of their job or micro-task and how it affects the overall company’s success. When they help improve the mental, emotional, or physical health of others, many people find that their work has a greater purpose. Awareness of their work and performance effects on others will inspire workers to put in more effort and perform better. The recognition they receive from others motivates them to achieve positive work outcomes.
Autonomy
In a job, autonomy refers to an employee’s ability to work independently. Management, supervisory, and ministerial roles often enjoy greater independence. In addition, employees who are allowed to take personal initiative can also develop a strong sense of responsibility and autonomy. A logistics coordinator might be free to select the best shipping routes or bargain with suppliers to cut expenses. Given the freedom to take responsibility for their work, employees feel motivated and creative. The freedom to plan the workday and establish new procedures increases a sense of responsibility.
Feedback
Feedback refers to how well workers are informed about their performance in a timely, precise, and transparent manner. Regarding business operations, staff members are given regular feedback on their work, enabling them to modify and enhance it. To improve their methods and procedures, a quality assurance analyst could get input on the dependability and correctness of their data analysis. Feedback encourages lifelong learning and growth, raising performance and job satisfaction.
The Psychological Component of the Job Characteristics Model
The second key component of the Job Characteristics Model (JCM) is psychological states. These refer to the degrees of employee motivation and satisfaction while executing a specific task or job.
Hackham and Oldham distinguished three of these states:
1. Meaningfulness
The extent to which an employee perceives their work as intrinsically valuable and significant, which enhances the experience, is known as the experienced meaningfulness of the work.
Three job characteristics contribute to meaningfulness: skill variation, task identity, and task importance.
2. Responsibility for Outcome
The degree of autonomy a work provides and requires shapes the experienced sense of responsibility.
3. Knowledge of Results
Feedback systems in an organization help to form knowledge of results. It shows how much straightforward and understandable information is given to the task holder regarding the efficacy of their performance.
Work-related Results Component of the Job Characteristics Model
In the final part of the Job Characteristics Model, the five core job characteristics are combined with the three psychological states to produce the following results:
- High Performance
- High Motivation
- High Satisfaction
JCM Indexing Scores
All five indicators receive scores, which are subsequently combined. This figure serves as an index for the overall motivational potential of the task or employment under consideration. The index number will show how much the job influences an employee’s behavior and attitude.
The index figure is known as the Motivating Potential Score, or MPS. The following formula can be used to determine the MPS:
MPS = (skill variety + task identity + task significance) / 3 autonomy feedback
Hackman and Oldham say that a low MPS score indicates that workers lack solid intrinsic motivation and that the activity or job needs to be modified.
The equation suggests that autonomy and feedback have a more significant influence on motivation than the other variables.
Additionally, Hackman and Oldham say workers can only go through the three psychological states if they score highly on the five indicators.
Benefits of Job Characteristic Model
The primary advantage of JCM is that it gives experts a template to use when designing jobs using the five core characteristics. Organizations can benefit from the job characteristics model in the following ways:
- It helps to design job strategies.
- JCM enhances job satisfaction.
- It Ensures job enrichment.
- There is better task delegation.
- There is clear organizational information.
- Goal setting and appraisals are straightforward.
In conclusion, developing a positive and effective work environment in business operations requires understanding and utilizing a job characteristics model. Organizations can promote a culture of engagement, motivation, and success by prioritizing skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback.
